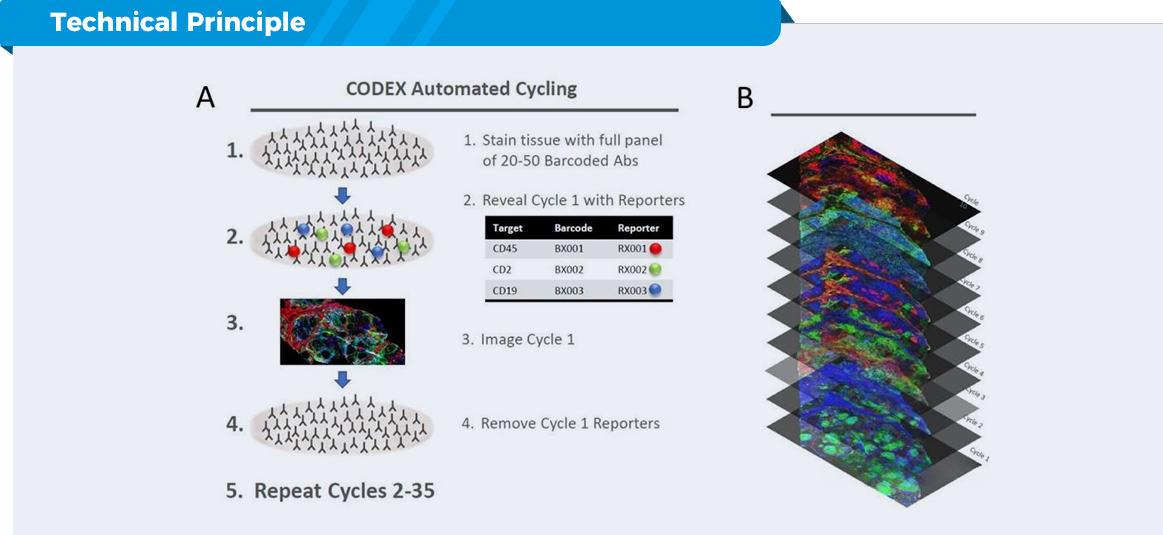
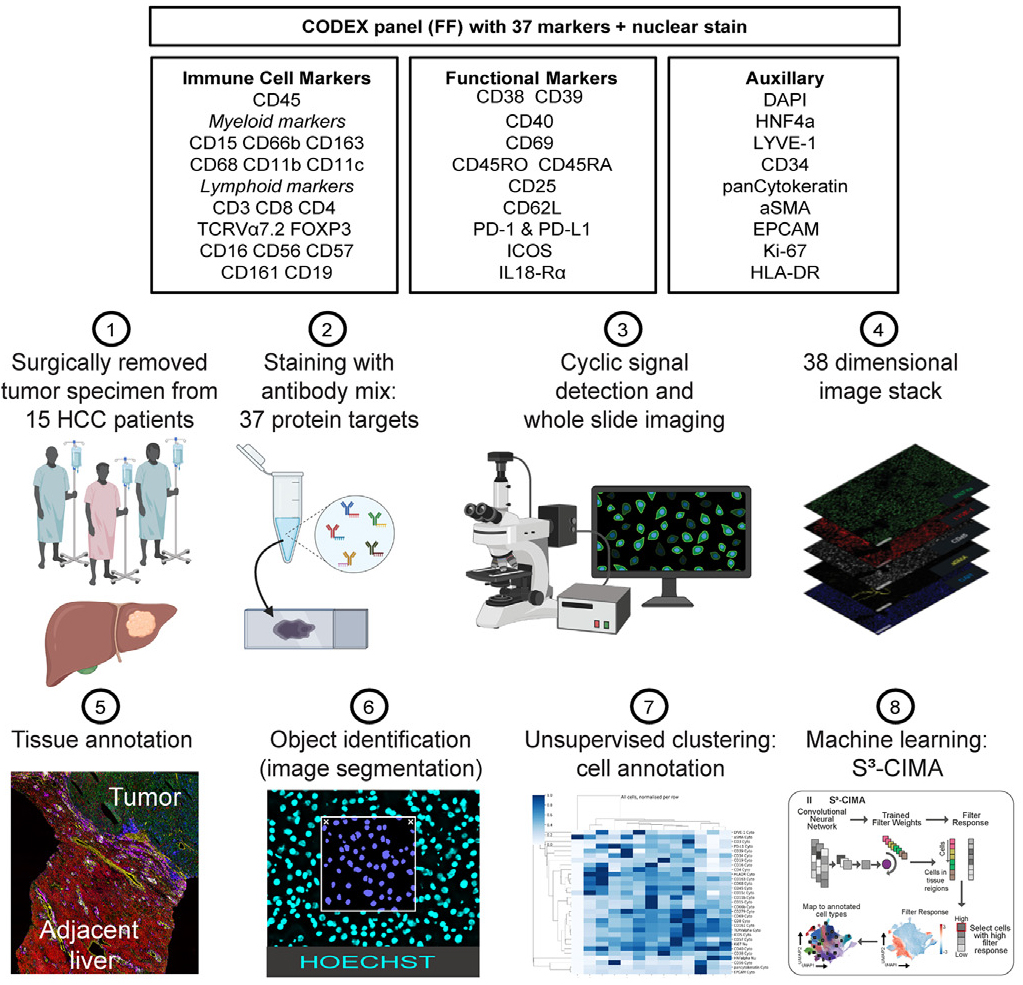
Complementary fluorescent molecular detection by coupling antibodies to specific Barcode nucleic acid molecules enables automated staining, imaging detection and spatial distribution data of up to 50+ target proteins on sectioned samples.
A wide range of sample types, from difficult to obtain free cell samples, to precious FFPE samples or frozen tissue sections.
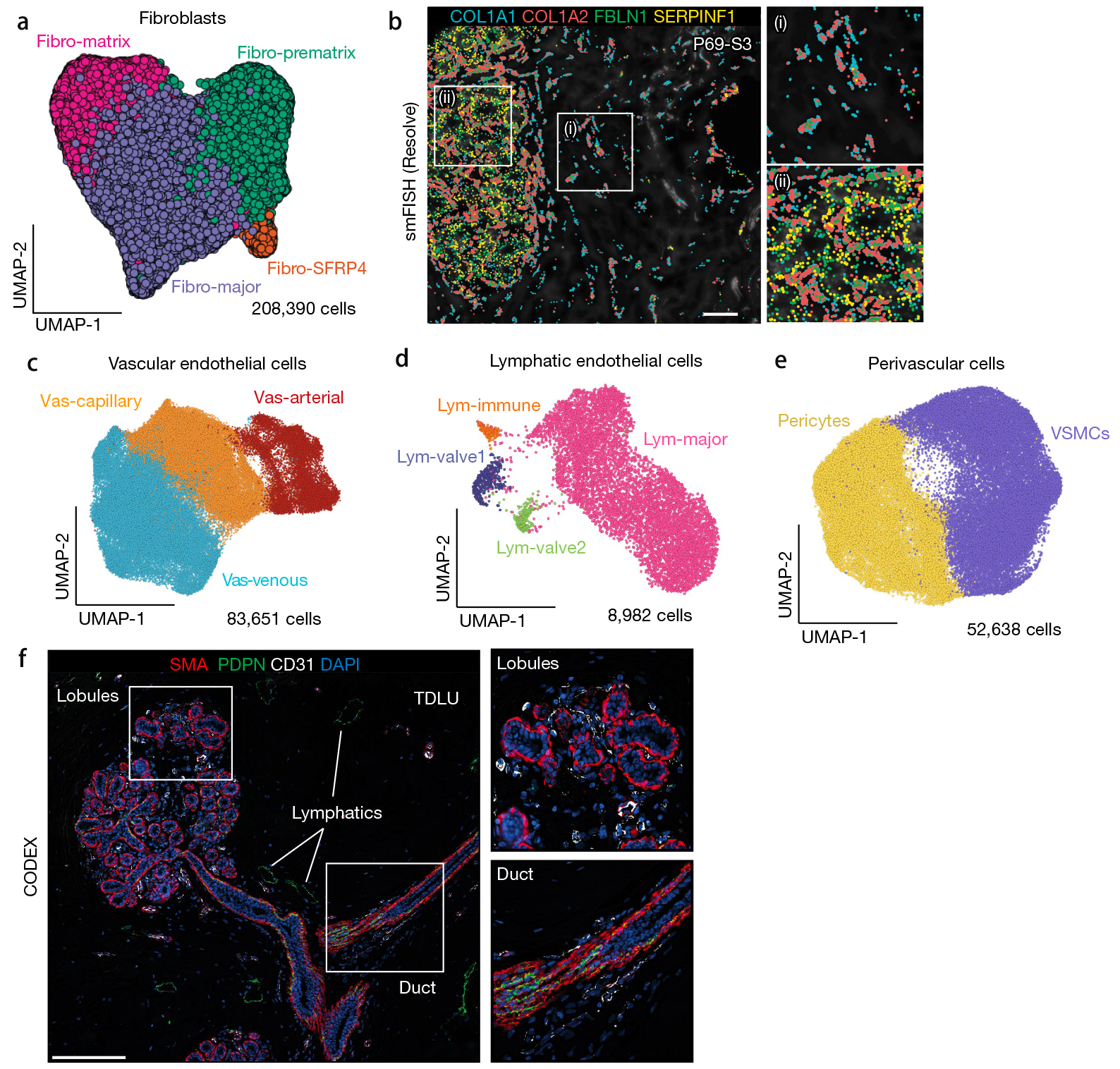
Cellular mapping
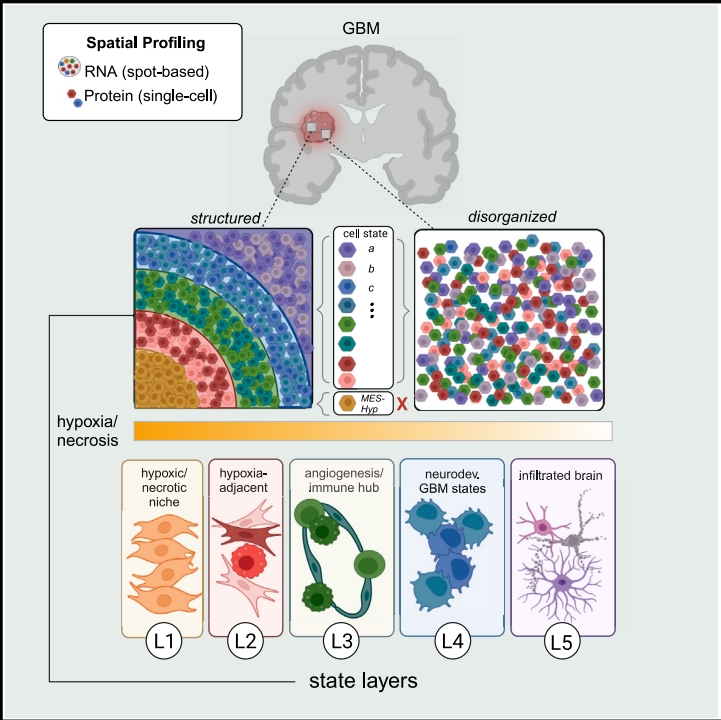
Discovering and mapping cell types using expression profiles of known RNA and protein targets
Tissue microenvironment
Understanding cellular fields by examining individual cells and their interacting neighboring cells
Biomarker discovery
Uncovering differential gene expression and pathways at different spatial locations in the same cell type
Disease state
Visualize and quantify changes in molecular (RNA/protein) and cellular organization in tissues
Ligand-receptor interaction
Analysis of up to 100 pairs of classical ligand-receptor interactions and expression in connected cells
COPYRIGHT©Infinity Scope Multi-Omics Biotechnology Co. Ltd., All rights reserved. 浙ICP备2024079019号-1